
5 Ways to Engage Employees During AI Rollout
Turn employee anxiety into enthusiasm with proven strategies that boost AI adoption rates and build workplace trust from day one.

Written by
Adam Stewart
Key Points
- Host peer-to-peer demos instead of generic training sessions
- Reduce performance expectations during the learning phase
- Share real wins and failures to build trust
- Create structured knowledge-sharing sessions to prevent shadow AI use
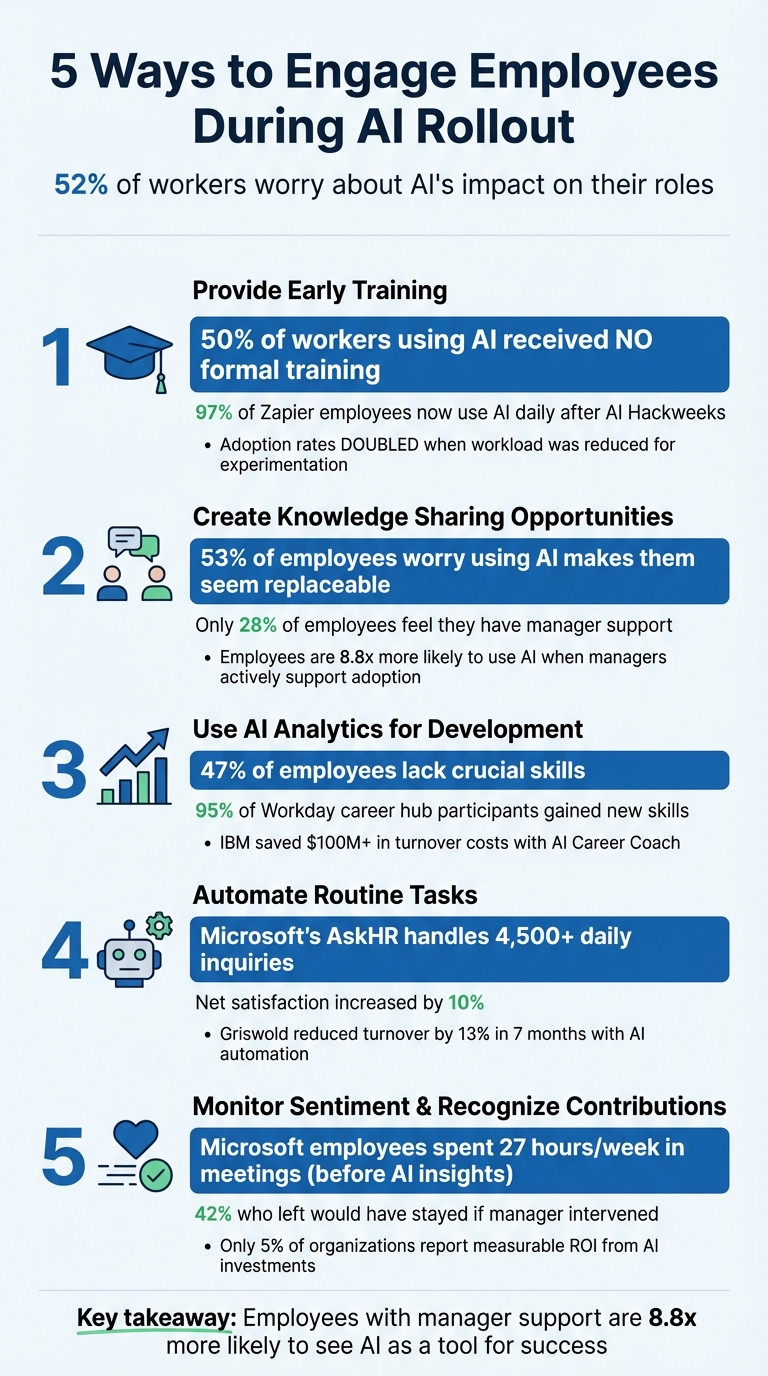
Introducing AI into the workplace can create anxiety for employees. Concerns about job disruption, surveillance, and being replaced are common, with 52% of workers worried about AI's impact on their roles. To address this, organizations must focus on building trust and involving employees in the process.
Here are five actionable strategies to ease the transition and help employees see AI as a tool, not a threat:
- Provide Early Training: Offer hands-on learning opportunities, real-world examples, and time to experiment with AI tools.
- Encourage Knowledge Sharing: Create spaces for employees to share AI insights, host demo days, and establish AI councils.
- Personalize Development: Use AI analytics to identify skill gaps and create tailored growth plans.
- Automate Routine Tasks: Free employees from repetitive work, allowing them to focus on meaningful contributions.
- Monitor Sentiment and Recognize Efforts: Use AI to gauge employee feedback and ensure contributions are acknowledged.
Key takeaway: Engaging employees early, offering support, and framing AI as a partner can transform fears into opportunities for growth and productivity.
5 Strategies to Engage Employees During AI Rollout with Key Statistics
1. Provide Early Training on AI Tools
Too often, companies introduce AI tools to their teams without offering any real training. In fact, half of workers using AI say their organization didn’t provide formal training [10]. It’s like handing someone the keys to a car without teaching them how to drive.
Early, structured training does more than just explain the basics - it helps employees overcome the unease that comes from working with something they don’t fully understand. When people grasp what AI can and can’t do - such as its tendency to fabricate information - they’re more likely to use it wisely. As Ronnie Sheer aptly puts it: "AI is 97% accurate but 100% confident" [7].
Practical examples show how hands-on training can speed up AI adoption. Take Workday’s "EverydayAI" initiative in May 2024, where nearly 20,000 employees were upskilled in AI. Chief People Officer Ashley Goldsmith used feedback from focus groups to encourage managers to set aside time for employees to experiment and even make mistakes with AI tools. The standout strategy? Peer-to-peer demos of real AI use cases worked far better than generic training sessions [9]. Watching colleagues solve actual problems helped employees connect the dots in ways a corporate slideshow never could.
Zapier also embraced a hands-on approach with its "AI Hackweeks." Cross-functional teams spent several days building AI-powered solutions together. The outcome? 97% of their employees now use AI daily [10]. That’s not just coincidence - it’s what happens when people are given the time, tools, and encouragement to learn.
Another key lesson: adjust performance expectations during the rollout. A software development firm discovered that while 80% of their developers were excited about AI, only 25% actually started using it. Why? Time pressure. To address this, the company temporarily reduced workloads, freeing up half of employees’ time for experimentation. The result? Adoption rates doubled [6]. You can’t expect people to master new tools while maintaining their usual productivity levels - something has to give.
2. Create Opportunities for Team Knowledge Sharing
Training might introduce the basics of AI, but it’s peer-to-peer knowledge sharing that keeps the momentum alive. When employees see a colleague tackle a real-world problem using AI, it resonates in a way that formal training simply can’t. Lilach Mollick, Co-Director of the Generative AI Lab at Wharton School, puts it perfectly:
"No one knows the best way to work with generative AI. There is no instruction manual. People are using it in radically different ways, depending on their areas of expertise" [11].
This kind of ongoing exchange of ideas and strategies pushes teams beyond the initial learning phase, fostering an environment where innovation can thrive.
But here’s the catch: without structured opportunities to share, employees often end up working in silos, leading to what’s known as "shadow AI." This isolated use of AI means your organization misses out on valuable insights that could improve workflows across the board [11]. The solution? Build regular opportunities for teams to share experiences, troubleshoot, and embrace the trial-and-error process of learning AI.
One idea is to host monthly demo days. These sessions allow employees to showcase their successes - and even their failures - while highlighting the importance of experimentation. When managers participate by sharing their own missteps alongside their wins, it sends a clear message: trying (and failing) is part of the process [8]. This is especially important when 53% of employees worry that using AI for key tasks might make them seem replaceable [4]. Seeing leadership engage in the same learning journey helps reframe AI as a tool for growth, not a threat.
Another approach is to establish an AI Council. This group, made up of representatives from HR, IT, legal, and management, can meet monthly to discuss AI strategies and challenges. Pair this with quick weekly check-ins where teams share recent AI applications or discoveries [1] [8].
The benefits are clear. When managers actively support AI adoption, employees are 8.8 times more likely to use AI to enhance their strengths. Yet, only 28% of employees feel they have that support [5]. Consistent knowledge-sharing initiatives can bridge this gap, creating a culture of collaboration and visible encouragement.
3. Use AI Analytics to Customize Employee Development
When nearly half of employees - 47% to be exact - lack crucial skills, generic training simply doesn’t cut it [2]. This is where AI analytics steps in, offering a smarter way to identify gaps and create personalized development plans that align with individual career aspirations.
AI tools can do a lot more than just crunch numbers. For instance, they use natural language processing to spot missing skills [2], track performance metrics to identify areas of underperformance [12], and even analyze meeting notes to highlight areas where confidence might be lacking [1]. The result? A highly specific, data-driven understanding of what each employee needs to grow. These insights don’t just sit in a report - they translate directly into actionable career opportunities.
Take Workday’s AI-powered "career hub" as an example. Back in 2019, it connected employees to short-term projects tailored to their development needs, and 95% of participants reported gaining new skills [13]. IBM’s "Career Coach" is another success story, predicting internal career moves and saving the company over $100 million by reducing turnover [13].
The key is making these insights meaningful. Joey Rubin, Head of Product Learning at ChangeEngine, explains it perfectly:
"People engage when they see a future for themselves" [1].
Imagine this: instead of sifting through a generic library of training videos, employees are offered a focused two-to-three–hour learning path tailored to an upcoming project. That kind of relevance makes the training feel valuable and immediately applicable.
To make it practical, companies can let employees view and update their AI-generated skill profiles [1], giving them a sense of ownership. AI can also match employees with internal mentors who excel in the skills they’re trying to develop [2]. This isn’t about surveillance; it’s about showing employees that AI is a tool for their growth. By tying development directly to career advancement, AI analytics help employees feel empowered, competitive, and ready for what’s next. Instead of fearing change, they’re prepared to embrace it.
sbb-itb-ef0082b
4. Automate Routine Tasks to Enable Higher-Value Work
Repetitive tasks can sap energy and enthusiasm from employees. When team members are bogged down with answering the same questions, handling help desk tickets, or managing routine phone calls, it leaves little room for the kind of work that drives real progress. This is where AI automation steps in, taking over these mundane responsibilities and freeing employees to focus on tasks that truly matter.
The numbers speak for themselves. In January 2025, Microsoft revealed that its AI platform, AskHR, processes more than 4,500 daily inquiries about benefits and policies. This automation not only streamlined operations but also boosted the company’s net satisfaction rating by nearly 10% [2]. Similarly, Griswold, a home care franchise, used predictive analytics and automation with Ava AI to cut its turnover rate by 13% in just seven months between June 2024 and January 2025 [2]. These examples highlight how targeting the right tasks for automation can make a meaningful difference.
Look for high-volume, repetitive tasks - like HR inquiries, IT password resets, or routine appointment scheduling - that consume time better spent on strategic initiatives. For customer-facing roles, tools like Dialzara can handle round-the-clock call answering, lead capture, and appointment booking, ensuring no opportunity is missed.
Tony Deblauwe, an HR leader and consultant, captures the essence of this shift:
"Reframe the message from 'AI is taking over X' to 'AI is here to support you in X so you can focus more on Y.' That shifts the tone from fear to empowerment." [4]
When employees view AI as a partner that helps them reclaim their time, rather than as a replacement, they’re more likely to embrace it. This allows them to dedicate their energy to strategic projects, creative endeavors, and personalized coaching - work that feels meaningful and impactful.
To get started, consider piloting automation in a single department. Use surveys to pinpoint low-value tasks, introduce AI solutions to handle them, and measure the results. When employees spend less time on busywork and more on meaningful contributions, the benefits of automation become clear, and adoption naturally grows.
5. Use AI to Monitor Sentiment and Recognize Contributions
The introduction of AI in workplaces often stirs up employee concerns, making it essential to monitor sentiment and acknowledge contributions in a timely manner [4]. By combining task automation with data-driven insights, organizations can better understand how employees feel and take action when needed.
AI-powered sentiment analysis tools, driven by Natural Language Processing (NLP), can evaluate survey responses, Slack messages, and emails in real time. This means you don’t have to wait for annual surveys to detect dissatisfaction. For example, between 2015 and 2018, Microsoft analyzed employee calendars and emails in one underperforming division. They found that workers were spending an average of 27 hours per week in meetings. This insight led to changes in meeting policies and quicker internal transfers, improving overall engagement [15]. It’s worth noting that 42% of employees who voluntarily left their jobs said they would have stayed if their manager had intervened [2].
AI tools also help managers recognize contributions more effectively. By scanning updates and collaboration threads, these tools can send managers notifications when a team member solves a critical issue or hasn’t been acknowledged in a while [2]. Some advanced systems even flag unconscious bias or gendered language in recognition messages before they’re sent, ensuring fairness and inclusivity [2].
Transparency is crucial when using AI in this way. Employees need to know what data is being collected and how it will be used. Sarah Marrs, Director of EX Strategy Execution at Qualtrics, explains:
"Generally, the more positive you feel about your organization – the more trust you have in it – and the more senior your role, the more likely you are to believe that your organization will use AI for your benefit" [14].
To maintain trust, aggregate data at the team level to protect individual anonymity, and involve human oversight for sensitive topics. AI can sometimes misinterpret sarcasm or regional language nuances, so human input remains vital [1][3].
When employees feel recognized and valued during an AI transition, they’re more likely to see the technology as an ally rather than a threat. To get started, try piloting a sentiment monitoring tool in one department. Use the insights to provide timely recognition and share the outcomes with the rest of the organization. This approach can pave the way for broader acceptance of AI and foster a more supportive workplace culture.
Conclusion
Rolling out AI successfully depends on collaboration with employees, not imposing changes on them. When workers feel left out of the process, they often see AI as a threat. This can lead to "quiet resistance", where they hold back valuable insights or offer only surface-level feedback [4]. The numbers back this up - just 5% of organizations report measurable ROI from their AI investments, often because adoption falters when employees don’t understand the value [5].
The key to overcoming this challenge lies in clear communication and proper guidance. By being transparent about what data is collected, involving employees early in the decision-making process, and offering training tailored to specific workflows, companies can reframe AI as a helpful ally rather than an intimidating change [4][5].
When AI is positioned to complement human work, it can free employees from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more meaningful responsibilities. This shift doesn’t just improve efficiency - it also boosts job satisfaction. Research shows that employees who feel supported by their managers in using AI are 8.8 times more likely to see it as a tool that helps them succeed [5].
To make this transition smoother, fostering psychological safety and open communication is essential. Regular feedback loops and clear guidelines on how to use AI appropriately can help teams adapt [8]. Managers play a critical role here - they should lead by example, sharing both successes and setbacks to normalize the learning process [8]. As Leann Stone, Director of HR Operations at Prescott HR, puts it:
"AI is as much a human transformation as a technical one" [4].
FAQs
How can AI training help reduce employee concerns during implementation?
AI training can turn hesitation into confidence by giving employees a clear understanding of how the technology works and integrates into their daily responsibilities. Interactive experiences like live workshops or hands-on demos allow staff to grasp the tool's purpose, how it processes data, and where their input remains essential. This approach helps address common concerns, such as, "Will this take over my job?" while encouraging a sense of involvement and control.
Take Dialzara’s AI-powered virtual phone answering service as an example. Role-specific training can show how the system manages tasks like handling calls, transferring them, and scheduling appointments. Employees get to explore its features in a relaxed setting, seeing for themselves how it improves workflows rather than replacing their efforts. This kind of practical experience, paired with ongoing support, builds trust, reduces anxiety, and promotes smooth adoption during implementation.
Why is knowledge sharing important for successful AI adoption?
Knowledge sharing plays a key role in making an AI rollout a team effort and ensuring its success. When managers and leaders take the time to clearly explain how AI tools function, why they’re being introduced, and how they’ll integrate into daily workflows, employees feel more at ease and less uncertain about the changes. This openness not only eases concerns about job security but also encourages employees to explore and engage with the technology.
To encourage knowledge sharing, consider organizing demo sessions, cross-department workshops, or informal Q&A forums. These activities help everyone gain a clearer understanding of AI, identify practical applications, and provide valuable feedback to refine the implementation process. By fostering trust and collaboration, such efforts pave the way for a smoother and more effective adoption of AI throughout the organization.
How can AI help create personalized employee development plans?
AI has the ability to dive into data like performance metrics, skill sets, project histories, and even learning preferences to uncover what each employee needs to grow. Through machine learning, it can spot skill gaps, anticipate future demands, and suggest customized training programs or hands-on learning opportunities.
What’s more, AI takes personalization to the next level. It can offer career path recommendations, provide AI-driven coaching, and flag skill gaps as they arise. It suggests courses that align with both personal goals and business objectives, while AI-powered mentorship tools connect employees with mentors who fit their development plans. The outcome? A flexible, personalized learning journey that keeps employees engaged, helps them build skills faster, and ties individual growth to the company’s overall success.
Summarize with AI
Related Posts
5 Benefits of AI in Performance Management
Explore how AI enhances performance management with data-driven evaluations, efficient processes, real-time feedback, and improved HR decision-making.
Common Problems AI Sentiment Analysis Solves in HR
AI sentiment analysis transforms HR by providing real-time insights into employee engagement, feedback, and turnover trends.
AI-Driven Employee Turnover Prediction: Guide
Learn how AI-driven employee turnover prediction can help organizations retain top talent, reduce costs, and maintain productivity. Explore the benefits, steps, and ethical considerations in this comprehensive guide.
AI Customer Service: Team Training & Change Management
Explore strategies for integrating AI in customer service with team training, change management, and best practices for a successful AI-powered support system.
